Improving Forecast Accuracy with Time Series Decomposition in Mobility Analytics
- Akira Oyama
- May 23, 2025
- 2 min read

Accurate forecasting is essential for businesses managing telecom expenses. Whether you're tracking smartphone data usage or IoT connectivity patterns, understanding what drives your mobility data - and how - is the first step toward selecting the right forecasting model.
A core challenge is that mobility data is rarely straightforward. It often includes:
Long-term growth trends
Seasonal usage spikes
Unexpected noise like network outages or promotional surges
This is where decomposition comes in.
What is Time Series Decomposition?
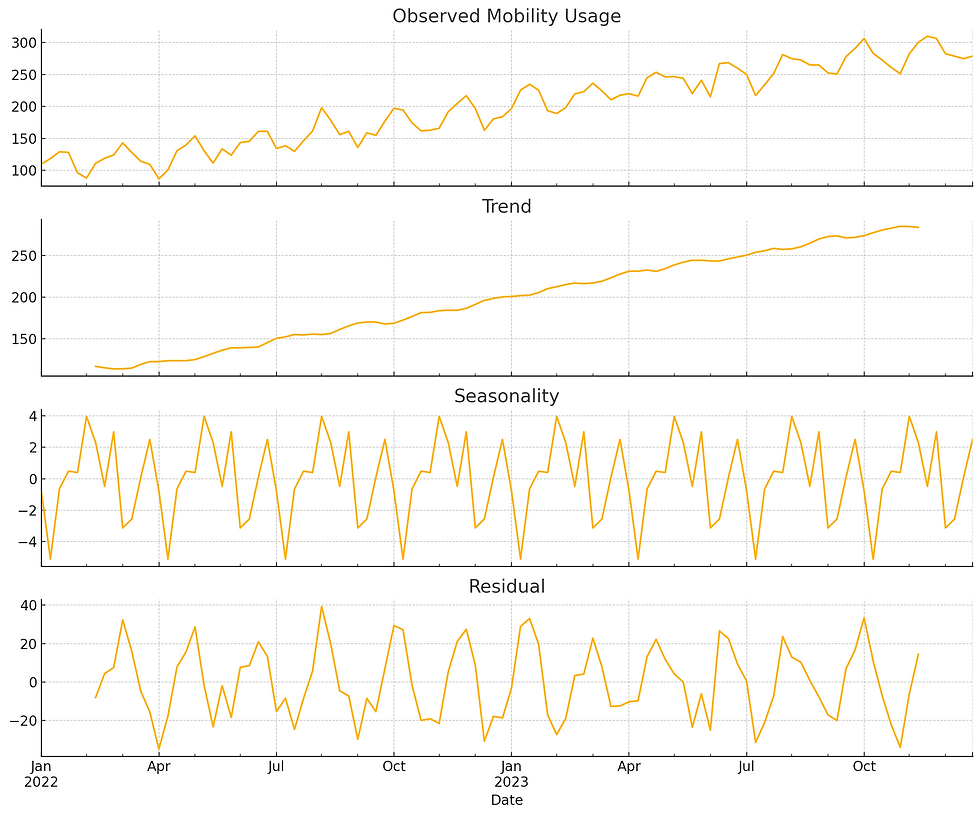
Decomposition breaks a time series into three components:
Trend - The long-term direction of usage (e.g., steady increase in IoT devices)
Seasonality - Repeating, predictable patterns (e.g., higher usage during holidays)
Residual (Noise) - Irregular variations due to one-off events
By isolating these components, you gain clarity on what's driving changes. This makes it easier to:
Understand historical behavior
Identify anomalies
Select the right forecasting method
Here's what a decomposition might look like:
Choosing the Right Forecasting Model
Once you've decomposed your data, you can better match forecasting models to patterns in your data. Here's a simple guide:
Situation | Recommended Model | Notes |
Clear trend, no seasonality | Holt's Linear Trend | Captures upward/downward trends |
Trend + seasonality | Holt-Winters (Triple Exponential Smoothing) | Works well with additive or multiplicative seasonality |
Complex patterns, autocorrelation | ARIMA/SARIMA | Power, but needs tuning |
Recent values most important | Simple Moving Average | Very basic, short horizon |
Deep learning or large-scale data | Prophet or LSTM | For more advanced needs |
Case Example: Holt-Winters Forecasting
In our sample mobility dataset, we observed both trend and seasonal effects - making Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing the ideal choice. It's:
Capable of modeling trend and seasonality
Easy to interpret and deploy
Well-suited for short- to medium-term forecasting
Here's how the model performs:

Conclusion
Decomposition isn't optional - it's essential.
Without it, you're guessing which model to use. With it, you understand:
How your data behaves
What drives changes
What model best fits your needs
Taking the time to decompose your mobility data enables smarter forecasting and better business decisions. Whether it's smartphones or IoT traffic, understanding trend, seasonality, and noise is the foundation of predictive accuracy.





Comments